health
5 tips to prevent and manage ulcerative colitis
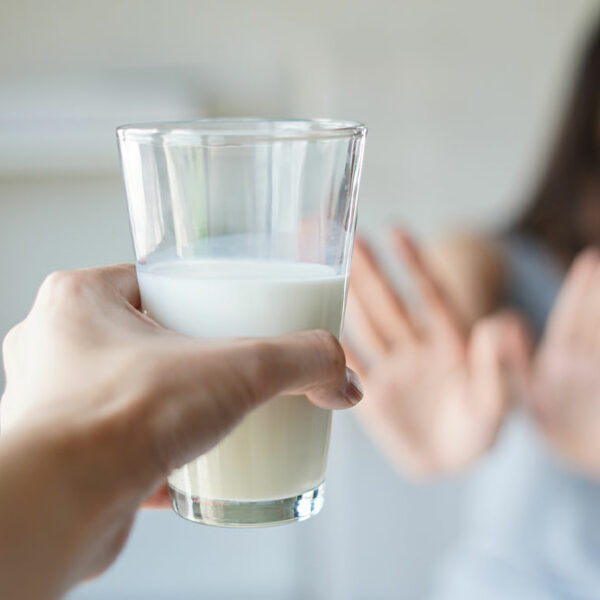
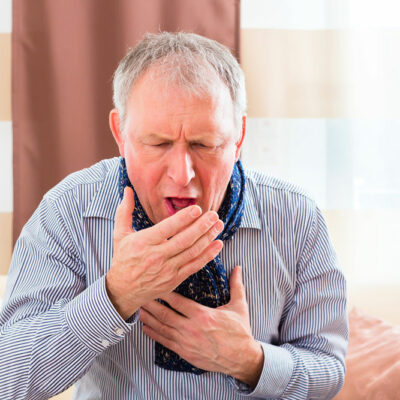
Ulcerative colitis is a long-term inflammatory disease that triggers inflammation and ulcers in the digestive system. It impacts the colon and rectum’s innermost lining. The symptoms are typically produced over a period rather than unexpectedly. According to the latest studies, about 1 million people have ulcerative colitis, and if left untreated, it can be crippling and cause life-threatening conditions. So, here are 5 tips to prevent and manage ulcerative colitis: Get on with the treatment plan immediately Even though there is no concrete cure for ulcerative colitis, proper treatment can help ease the symptoms and signs of the condition and eventually provide long-term remission. If a patient feels that their bowel habits are consistently changing or if they experience any of the following symptoms and signs, they should immediately consult a doctor: Blood in stool Ongoing diarrhea that is not getting cured by any other types of treatments An unknown fever going on for more than a day or two Abdominal pain Diarrhea that wakes up the patient from sleep The treatments prescribed by the doctor will typically include a combination of oral therapy or surgery. As far as oral treatments are concerned, the doctor may prescribe any of the following types of therapies, depending on the patient’s existing condition:
Read More